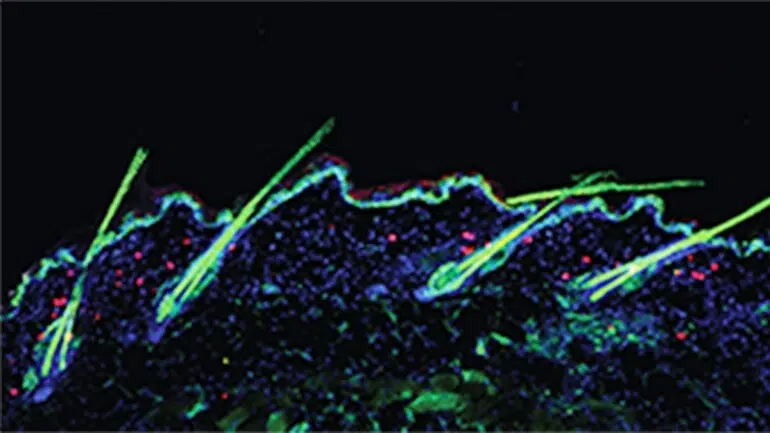
 In experiments in mice, UC San Francisco researchers have discovered that regulatory T cells (Tregs; pronounced “tee-regs”), a type of immune cell generally associated with controlling inflammation, directly trigger stem cells in the skin to promote healthy hair growth. Without these immune cells as partners, the researchers found, the stem cells cannot regenerate hair follicles, leading to baldness.
In experiments in mice, UC San Francisco researchers have discovered that regulatory T cells (Tregs; pronounced “tee-regs”), a type of immune cell generally associated with controlling inflammation, directly trigger stem cells in the skin to promote healthy hair growth. Without these immune cells as partners, the researchers found, the stem cells cannot regenerate hair follicles, leading to baldness.
“Our hair follicles are constantly recycling: when a hair falls out, a portion of the hair follicle has to grow back,” said Michael Rosenblum, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of dermatology at UCSF and senior author on the new paper. “This has been thought to be an entirely stem cell-dependent process, but it turns out Tregs are essential. If you knock out this one immune cell type, hair just doesn’t grow.”
Defects in Tregs responsible
The new study – published online May 26 in Cell – suggests that defects in Tregs could be responsible for alopecia areata, a common autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss, and could potentially play a role in other forms of baldness, including male pattern baldness, Rosenblum said. Since the same stem cells are responsible for helping heal the skin after injury, the study raises the possibility that Tregs may play a key role in wound repair as well. Read the rest of the article at https://www.ucsf.edu
